Certificate-Based Authentication
Certificate-based authentication provides a more secure alternative to client secrets for service-to-service communication. AZExecute automates the entire certificate lifecycle - from generation to renewal to deployment - ensuring your applications maintain secure authentication without manual intervention.
Why Use Certificate Authentication?
Certificates offer several advantages over client secrets:
Enhanced Security: Certificate private keys are much harder to compromise than text-based secrets
Hardware Storage: Can be stored in HSMs or TPMs for additional protection
Better Governance: Certificates can be centrally managed and audited more effectively
Longer Lifetimes: Certificates can have much longer validity periods than secrets (up to 3 years)
Non-repudiation: Certificate signatures provide proof of authenticity
Enabling Certificate Management
To enable automated certificate management for an application:
1. Navigate to your application's details page
2. Go to the Certificates tab
3. Enable the Certificate Authentication toggle
4. Configure certificate settings (lifetime, renewal threshold)
5. Click Generate Certificate to create the first certificate
6. Optionally configure Key Vault integration for automatic deployment
7. Click Save Changes to activate

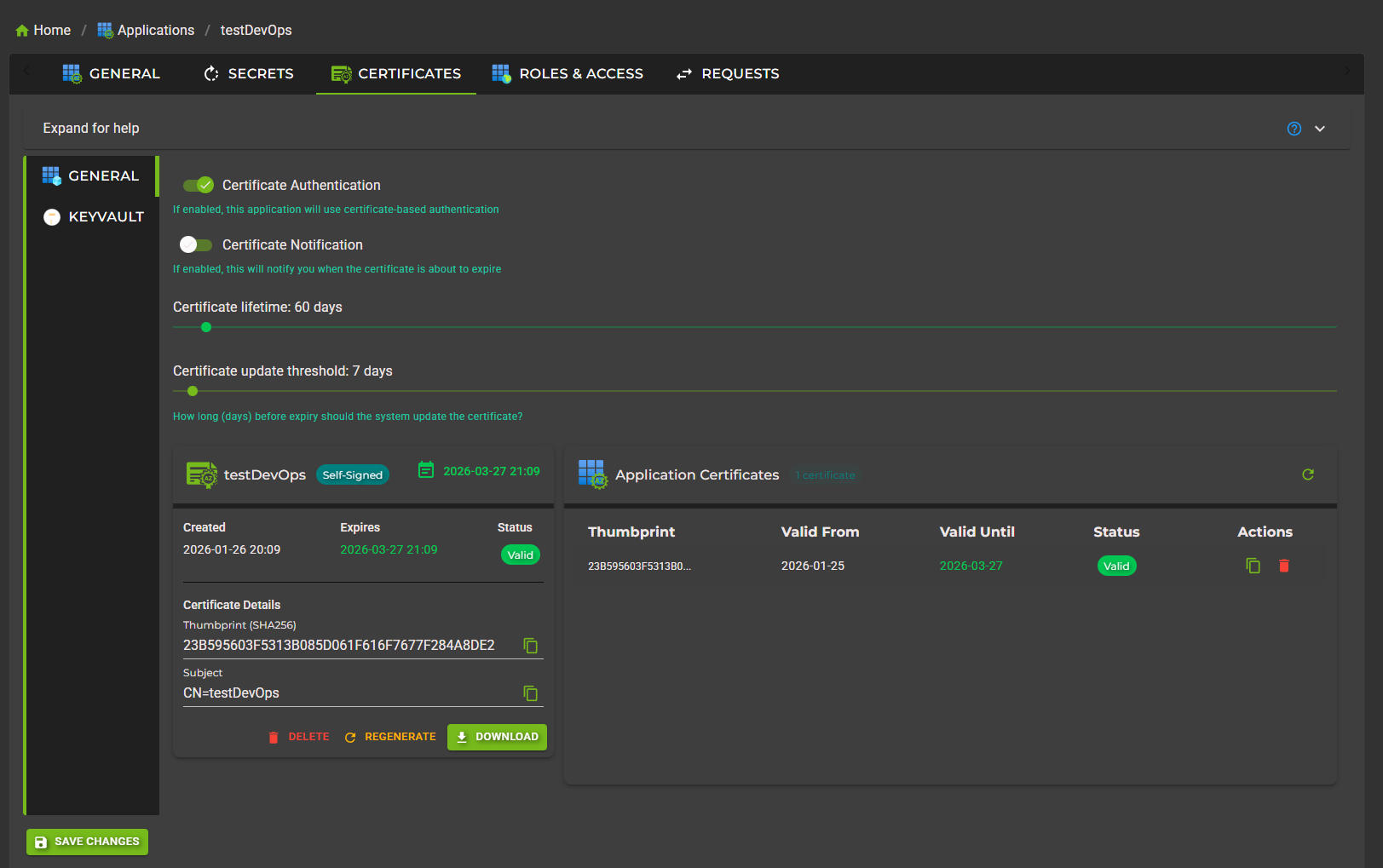
Certificate Configuration Options
Certificate Lifetime
Define how long each certificate remains valid before renewal is required.
Range: 30 to 1095 days (30 days to 3 years)
Recommended: 365 days (1 year) for production applications
Consideration: Longer lifetimes reduce maintenance but may not meet security policies
Update Threshold
Specify how many days before expiry the system should generate and deploy a new certificate.
Range: 1 to 365 days
Recommended: 30 days for certificates with 1-year lifetime
Purpose: Ensures smooth transition without service interruption
Certificate Notifications
Configure email alerts for certificate lifecycle events:
Enable notifications: Receive alerts about certificate renewals
Notification threshold: Set how many days before expiry to send alerts (1-90 days)
Include certificate in email: Optionally attach certificate data (PFX/PEM format)

Generating Certificates
AZExecute creates self-signed X.509 certificates optimized for Entra ID authentication:
Certificate Properties
Algorithm: RSA 2048-bit (industry standard)
Signature Hash: SHA-256
Subject Name: CN={ApplicationName}
Key Usage: Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
Enhanced Key Usage: Client Authentication
Generation Process
When you generate a certificate:
1
Private Key Generation
2048-bit RSA key pair is created using secure random number generation2
Certificate Creation
Self-signed certificate is created with configured lifetime and properties3
Entra ID Upload
Public certificate is uploaded to the Application Registration in Entra ID4
Secure Storage
Certificate and private key are encrypted and stored in AZExecute database5
Integration Deployment
If Key Vault integration is enabled, certificate is deployed to specified vaultCertificate Formats and Downloads
Certificates can be downloaded in multiple formats to support different platforms and use cases:
PFX Format (PKCS#12)
Contains: Certificate + Private Key (password protected)
Use for: Windows applications, IIS, Azure App Services
Security: Protected with strong random password displayed once
PEM Format
Contains: Separate certificate and private key files (Base64 encoded)
Use for: Linux applications, Python, Node.js, Java
Files: certificate.pem (public) and privatekey.pem (private)
CER Format (Public Only)
Contains: Public certificate only (no private key)
Use for: Verification, trust establishment, sharing public key
Security: Safe to distribute - cannot be used for authentication

Automatic Certificate Renewal
AZExecute automatically renews certificates before they expire, ensuring continuous authentication:
1
Renewal Check
Background service monitors certificate expiration dates every 15 minutes2
Threshold Evaluation
When current date reaches the update threshold window, renewal process begins3
New Certificate Generation
New certificate with fresh private key is created using same configuration4
Entra ID Update
New certificate is added to Application Registration (old one remains valid)5
Key Vault Deployment
If configured, new certificate is deployed to Key Vault as latest version6
Notification Sent
Email alerts sent to administrators if notifications are enabledKey Vault Integration
Automatically deploy certificates to Azure Key Vault for secure, centralized access:
Configuration Steps
1. On the Certificates tab, enable Key Vault Integration
2. Select the target Key Vault from your accessible vaults
3. System automatically configures necessary access (RBAC or Access Policies)
4. Certificate name in Key Vault defaults to application name (customizable)
5. Click Save Changes to activate integration
How It Works
Automatic Upload: New certificates are uploaded to Key Vault as PFX (includes private key)
Version Management: Each renewal creates a new certificate version in Key Vault
Access Control: Application service principal gets Certificate Get and Secret Get permissions
Application Retrieval: Apps use Key Vault SDK to retrieve current certificate

Managing Existing Certificates
View and manage all certificates associated with your application:
Certificate Table
The Certificates tab displays a table of all certificates in Entra ID for your application:
Display Name: Certificate identifier (usually "AutomationCert")
Thumbprint: Unique identifier for the certificate
Valid From: When the certificate becomes valid
Valid Until: Expiration date and time
Status: Current/Expired indicator
Deleting Certificates
You can manually delete certificates from Entra ID:
• Click the Delete button next to any certificate in the table
• Confirm the deletion (this is permanent)
• Certificate is immediately removed froEntra IDAD
Manual Certificate Regeneration
Manually generate a new certificate at any time:
1. Click the Generate New Certificate button
2. Confirm you want to create a new certificate
3. New certificate is generated and deployed (old one remains valid)
4. Download the new certificate or retrieve from Key Vault
Common scenarios for manual generation:
Certificate private key potentially compromised
Testing deployment and renewal processes
Changing certificate lifetime requires new certificate
Using Certificates in Applications
Applications retrieve and use certificates for authentication in different ways depending on the platform:
.NET Applications with Key Vault
using Azure.Identity; using Azure.Security.KeyVault.Certificates; using Microsoft.Identity.Client; // Retrieve certificate from Key Vault var kvUri = "https://myvault.vault.azure.net/"; var certClient = new CertificateClient(new Uri(kvUri), new DefaultAzureCredential()); var certificate = await certClient.DownloadCertificateAsync("MyAppCertificate"); // Use certificate for authentication var app = ConfidentialClientApplicationBuilder .Create(clientId) .WithCertificate(certificate) .WithAuthority(new Uri(authority)) .Build(); var result = await app.AcquireTokenForClient(scopes).ExecuteAsync();
Python Applications
from azure.identity import CertificateCredential from azure.keyvault.certificates import CertificateClient from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential # Retrieve certificate from Key Vault credential = DefaultAzureCredential() cert_client = CertificateClient( vault_url="https://myvault.vault.azure.net/", credential=credential ) certificate = cert_client.get_certificate("MyAppCertificate") # Use certificate for authentication cert_credential = CertificateCredential( tenant_id=tenant_id, client_id=client_id, certificate_path="path/to/certificate.pem" ) token = cert_credential.get_token("https://graph.microsoft.com/.default")
Node.js Applications
const { CertificateClient } = require("azure/keyvault-certificates"); const { DefaultAzureCredential } = require("azure/identity"); const { ConfidentialClientApplication } = require("azure/msal-node"); // Retrieve certificate from Key Vault const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential(); const client = new CertificateClient("https://myvault.vault.azure.net/", credential); const certificate = await client.getCertificate("MyAppCertificate"); // Use certificate for authentication const config = { auth: { clientId: clientId, authority: authority, clientCertificate: { thumbprint: certificate.properties.x509Thumbprint, privateKey: privateKeyPem } } }; const cca = new ConfidentialClientApplication(config); const result = await cca.acquireTokenByClientCredential({ scopes: scopes });
Best Practices
Use 1-year certificate lifetimes for production
Balance between security and operational overheadSet 30-day renewal threshold minimum
Provides ample time for testing and gradual rolloutAlways use Key Vault integration
Eliminates manual certificate deployment and managementConfigure applications to retrieve latest certificate version
Don't pin to specific certificate versions - use versionless Key Vault URIsTest certificate renewal in non-production first
Verify your application correctly handles certificate updatesEnable renewal notifications for critical applications
Stay informed about certificate lifecycle eventsStore certificate passwords securely if not using Key Vault
Use password managers or encrypted configuration for PFX passwordsMonitor certificate expiration actively
Review application logs regularly to catch renewal failures earlyTroubleshooting
Certificate Not Renewing Automatically
If automatic renewal isn't occurring:
• Verify Certificate Authentication is enabled on the Certificates tab
• Check that the application state is Active
• Review application logs for errors during renewal attempts
• Ensure the update threshold window has been reached
• Verify that a certificate already exists (system won't auto-create first one)
Key Vault Deployment Failed
If certificate is generated but Key Vault upload fails:
• Check application log for specific error details
• Verify Key Vault RBAC permissions or Access Policies are configured
• Ensure Key Vault firewall allows access from AZExecute
• Check that the Key Vault hasn't been deleted or moved
• Try manual generation to isolate the issue
Application Authentication Failing After Renewal
If your application stops authenticating after certificate renewal:
• Verify application is retrieving certificate from Key Vault (not using cached version)
• Check that application restart or reload occurred to pick up new certificate
• Ensure application is using versionless Key Vault URI (gets latest version)
• Verify the certificate thumbprint in authentication logs matches new certificate
• ChecEntra IDAD sign-in logs for specific authentication errors
Cannot Download Certificate
If certificate downloads are not working:
• Private keys are only available once at generation - use Key Vault for persistent access
• Public certificates (CER) can always be downloaded from the Certificates tab
• For full certificate with private key, generate a new one if needed
• Consider using Key Vault integration to avoid needing manual downloads
If you encounter any issues or need further assistance, please contact us at
info@azexecute.com. Our support team is here to help you.
